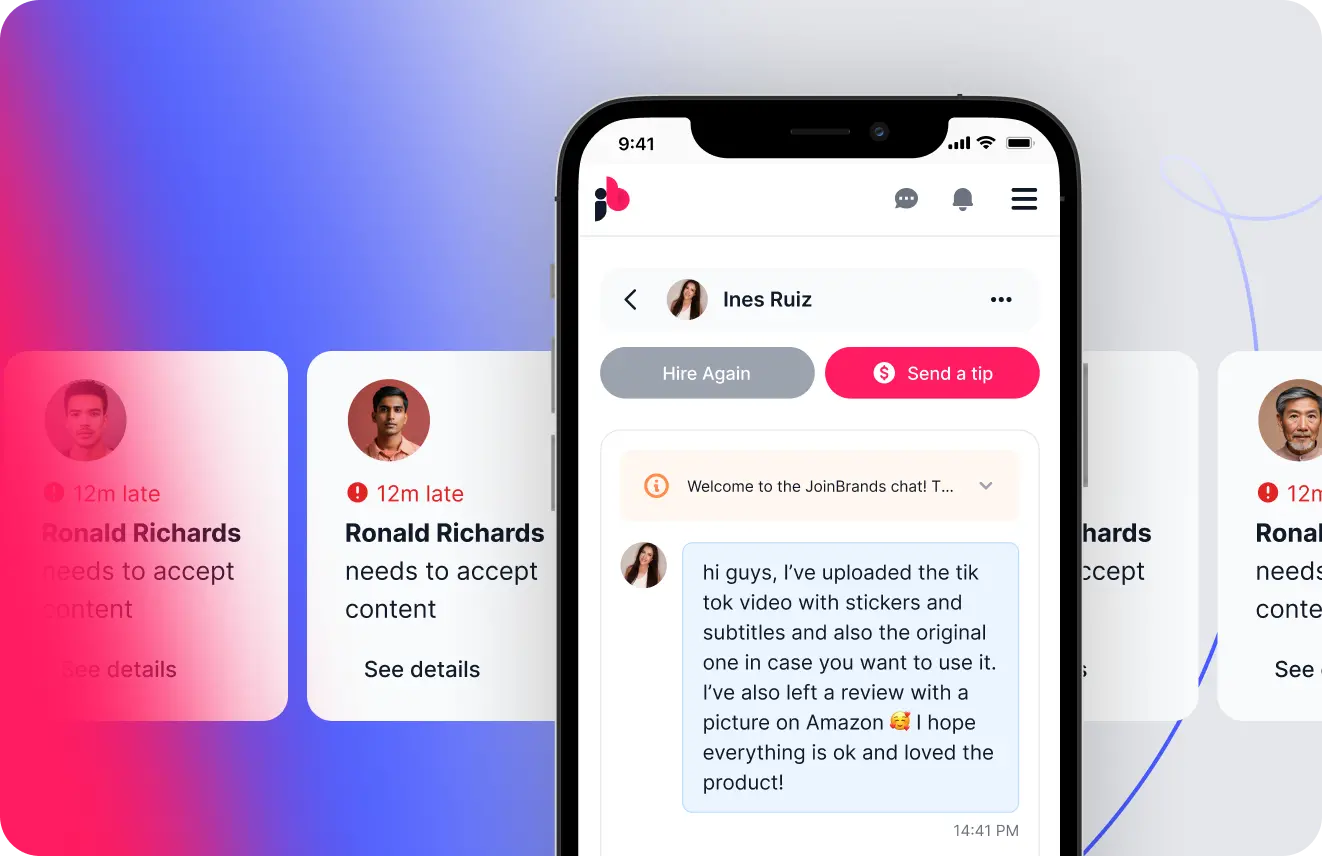
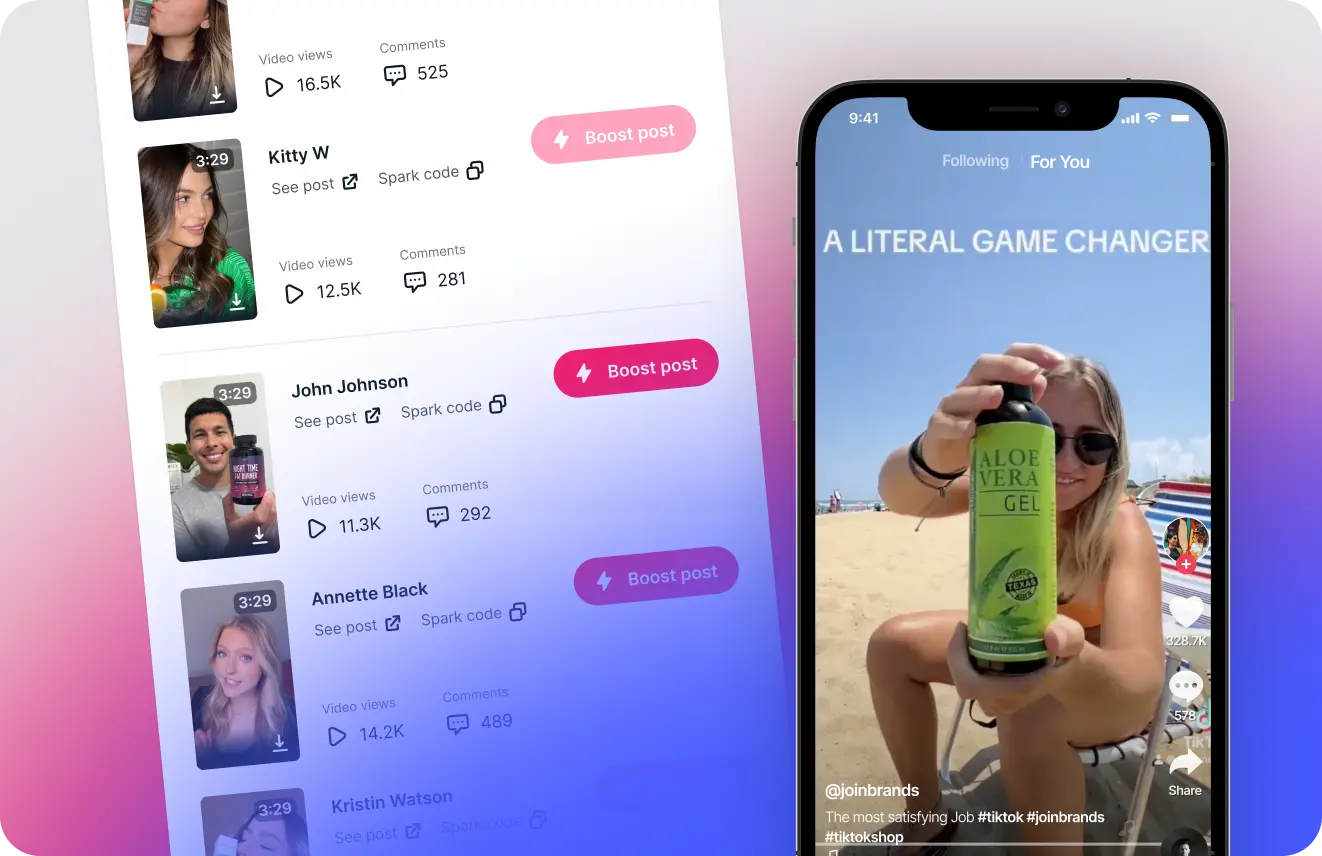
TikTok Shop Affiliates
TikTok Creators
Instagram Influencers
Amazon Influencers
YouTube Influencers
Social Media Managers
AI Creators
UGC Creators
TikTok Videos
UGC Content
TikTok Shop Affiliates
Amazon Shoppable
Social Media Blasts
Spark Ads
Instagram Reels
YouTube Shorts
B-Rolls
Product Launches
TikTok Shop Affiliates
TikTok Creators
Instagram Influencers
Amazon Influencers
YouTube Influencers
Social Media Managers
AI Creators
UGC Creators
TikTok Videos
UGC Content
TikTok Shop Affiliates
Amazon Shoppable
Social Media Blasts
Spark Ads
Instagram Reels
YouTube Shorts
B-Rolls
Product Launches